
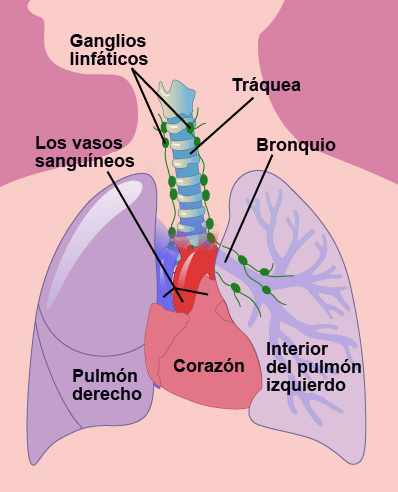
The present study aimed to determine whether the EAT volume (EV) and mean EAT attenuation (mEA) measured by non-contrast routine chest CT (RCCT) could be more consistent with those measured by coronary CT angiography (CCTA) by adjusting the threshold of fatty attenuation. contrast, it is important to understand, that there is a dual blood supply to the liver.BACKGROUND: Epicardial adipose tissue (EAT) is known as an important imaging indicator for cardiovascular risk stratification. On a non enhanced CT-scan (NECT) liver tumors are not visible, because the inherent contrast between tumor tissue and the surrounding liver parenchyma is too low. The conspicuity of a liver lesion depends on the attenuation difference between the lesion and the normal liver. So you start at 75 seconds with whatever scanner you have. Besides you have more time, because the delayed or equilibrium phase starts at about 3-4 minutes. Here you don't want to be too early, because you want to load the liver with contrast and it takes time for contrast to get from the portal vein into the liver parenchyma. In aterial phase imaging the time window is narrow, since you have only limited time before the surrounding liver will start to enhance and obscure a hypervascular lesion.įor Late portal venous phase imaging it is different. So you start scanning at about 33 seconds, which is much later. However if you have a 64-slice scanner, you will be able to examine the whole liver in 4 seconds. If you have a single slice scanner, it will take about 20 seconds to scan the liver.įor late arterial phase imaging 35 sec is the optimal time, so you start at about 25 seconds and end at about 45 seconds. You have to adapt your protocol to the type of scanner, the speed of contrast injection and to the kind of patient that you are examining. This is comparable to late enhancement of infarcted scar tissue in cardiac MRI. There is wash out of contrast in all abdominal structures except for fibrotic tissue, because fibrotic tissue has a poor late wash out and will become relatively dense compared to normal tissue. Sometimes called "wash out phase" or "equilibrium phase". Only in this phase you will be able to detect small renal cell carcinomas. This is when all of the renal parenchyma including the medulla enhances. In this phase the liver parenchyma enhances through bloodsupply by the portal vein and you should see already some enhancement of the hepatic veins. Although hepatic phase is the most accurate term, most people use the term "late portal phase". Hepatic or late portal phase - 70-80 sec p.i.All structures that get their bloodsupply from the arteries will show optimal enhancement. Sometimes also called "arterial phase" or "early venous portal phase", because some enhancement of the portal vein can be seen. This is the phase when the contrast is still in the arteries and has not enhanced the organs and other soft tissues. Non-enhanced CT (NECT) Helpful in detecting calcifications, fat in tumors, fat-stranding as seen in inflammation like appendicitis, diverticulitis, omental infarction etc.Scroll through the images to see the enhancement in the different phases. So it is important to know in which phase a CT should be performed depending on the pathology that you are looking for. Sometimes a lesion will be hypovascular compared to the normal tissue and in some cases a lesion will be hypervascular to the surrounding tissue in a certain phase of enhancement. The purpose of contrast-enhanced CT (CECT) is to find pathology by enhancing the contrast between a lesion and the normal surrounding structures.

TI-RADS - Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System.Esophagus II: Strictures, Acute syndromes, Neoplasms and Vascular impressions.Esophagus I: anatomy, rings, inflammation.Vascular Anomalies of Aorta, Pulmonary and Systemic vessels.Contrast-enhanced MRA of peripheral vessels.Ischemic and non-ischemic cardiomyopathy.Coronary Artery Disease-Reporting and Data System.Bi-RADS for Mammography and Ultrasound 2013.Transvaginal Ultrasound for Non-Gynaecological Conditions.Acute Abdomen in Gynaecology - Ultrasound.Appendicitis - Pitfalls in US and CT diagnosis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
